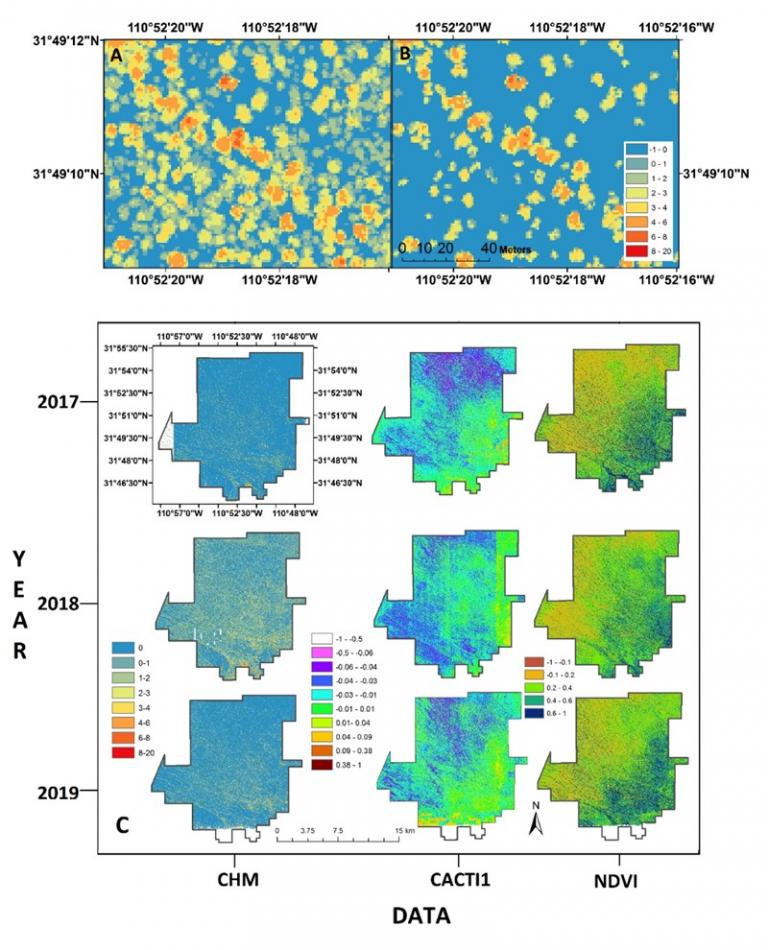
Multi-temporal Lidar and Hyperspectral Fusion for Classification of Woody Cover Species
Mapping the spatial distribution of woody vegetation is important for monitoring, managing, and studying woody encroachment in grasslands. However, discrimination of tree species is difficult due to the sparse canopy cover in semi-arid regions. Similar studies in different biomes have achieved low accuracies using coarse spatial resolution image data. The objective of this study was to investigate the use of multi-temporal, airborne hyperspectral imagery and light detection and ranging (LiDAR) derived data for tree species classification in a semi-arid desert region. This study produces highly accurate classifications by combining multi-temporal high spatial resolution hyperspectral and LiDAR data through a reproducible scripting approach that can be applied to larger areas and similar datasets. Combining multi-temporal vegetation indices and canopy height models led to an overall accuracy of 95.28% and kappa of 94.17%. Five woody species were discriminated resulting in producer accuracies ranging from 86.12% to 98.38%. The influence of fusing spectral and structural information in a random forest classifier for tree identification is evident. Additionally, a multi-temporal dataset slightly increases classification accuracies over a single data collection. Our results show a promising methodology for tree species classification in a semi-arid region using multi-temporal hyperspectral and LiDAR remote sensing data. Mapping the spatial distribution of woody vegetation is important for monitoring, managing, and studying woody encroachment in grasslands. However, discrimination of tree species is difficult due to the sparse canopy cover in semi-arid regions. Similar studies in different biomes have achieved low accuracies using coarse spatial resolution image data. The objective of this study was to investigate the use of multi-temporal, airborne hyperspectral imagery and light detection and ranging (LiDAR) derived data for tree species classification in a semi-arid desert region. This study produces highly accurate classifications by combining multi-temporal high spatial resolution hyperspectral and LiDAR data through a reproducible scripting approach that can be applied to larger areas and similar datasets. Combining multi-temporal vegetation indices and canopy height models led to an overall accuracy of 95.28% and kappa of 94.17%. Five woody species were discriminated resulting in producer accuracies ranging from 86.12% to 98.38%. The influence of fusing spectral and structural information in a random forest classifier for tree identification is evident. Additionally, a multi-temporal dataset slightly increases classification accuracies over a single data collection. Our results show a promising methodology for tree species classification in a semi-arid region using multi-temporal hyperspectral and LiDAR remote sensing data.